Jackdaw Corvus monedula
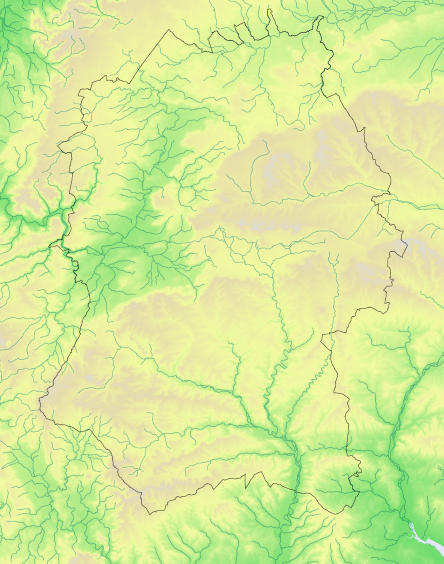
Breeding distribution change
Common and increasing resident in open or wooded country and towns
Atlas species lists
- Breeding distribution 1995–2000
- Summer abundance 1995–2000
- Winter distribution 1995–2000
- Winter abundance 1995–2000
- Breeding distribution 2007–2012
- Summer abundance 2007–2012
- Winter distribution 2007–2012
- Winter abundance 2007–2012
- Breeding distribution change
- Summer abundance change
- Winter distribution change
- Winter abundance change
More Jackdaw maps
- Breeding distribution 1995–2000
- Summer abundance 1995–2000
- Winter distribution 1995–2000
- Winter abundance 1995–2000
- Breeding distribution 2007–2012
- Summer abundance 2007–2012
- Winter distribution 2007–2012
- Winter abundance 2007–2012
- Breeding distribution change
- Summer abundance change
- Winter distribution change
- Winter abundance change
Map explanation
This map shows where changes occurred in the breeding season distribution of the species in Wiltshire between 1995-2000 and 2007-2012, as revealed by the fieldwork for Birds of Wiltshire (Wiltshire Ornithological Society 2007) and the shared fieldwork for Bird Atlas 2007-2011 (BTO 2013) and for Wiltshire Tetrad Atlas 2007-2012.
Gains and improvements
Status
Nos tetrads
Absent to present
21
2%

Present to breeding
123
13%

Absent to breeding
22
2%
No change
Status
Nos tetrads

Present in both
85
9%

Breeding in both
450
49%
Losses and declines
Status
Nos tetrads

Present to absent
26
3%

Breeding to present
153
17%

Breeding to absent
18
2%
Jackdaws are found from northwest Africa eastwards across much of Eurasia to Mongolia and Kashmir. In Europe they are absent only from Iceland, northern and inland Fenno-Scandia and northernmost Russia. Most are resident though some in the northern regions migrate WSW in autumn. In other colder regions they congregate near human habitation or warmer coastal areas.
In Great Britain they are largely sedentary. They are widespread except in Scotland where they are absent from large parts of the northwest mainland and some off-shore islands. They are most abundant south and west of a line drawn from the Wirral perinsula to Beachy Head.
In Wiltshire they have been common and abundant at least since the mid 19th century. Birds of Wiltshire recorded them present in summer in 855 tetrads (94%) with breeding in 621, figures that were scarcely changed in WTA2 (present in 854 tetrads, breeding in 595). There were only marginal differences between the summer and winter distribution figures in either atlas.
References
The following references are used throughout these species accounts, in the abbreviated form given in quotation marks:
“1968-72 Breeding Atlas” – Sharrack, J.T.R. 1976: The Atlas of Breeding Birds in Britain and Ireland. T. & A. Poyser
“1981-84 Winter Atlas” – Lack, P.C. 1986: The Atlas of Wintering Birds in Britain and Ireland. T. & A. Poyser
“1988-91 Breeding Atlas” – Gibbons, D.W., Reid, J.B. & Chapman, R.A. 1993: The New Atlas of Breeding Birds in Britain and Ireland 1988-91. T. & A. Poyser
“Birds of Wiltshire” – Ferguson-Lees, I.J. et al. 2007 : Birds of Wiltshire, published by the tetrad atlas group of the Wiltshire Ornithological Society after mapping fieldwork 1995-2000. Wiltshire Ornithological Society.
“Bird Atlas 2007-2011” – Balmer, D.E., Gillings, S., Caffrey, B.J., Swann, R.L., Downie, I.S. and Fuller, R.J. 2013: Bird Atlas 2007-2011: the Breeding and Wintering Birds of Britain and Ireland
“WTA2” – ("Wiltshire Tetrad Atlas 2 ") the present electronic publication, bringing together the Wiltshire data from “Birds of Wiltshire” and “Bird Atlas 2007-11”, together with data from further fieldwork carried out in 2011 and 2012.
"Hobby" - the annual bird report of the Wiltshire Ornithological Society.