Atlas species lists
- Breeding distribution 1995–2000
- Summer abundance 1995–2000
- Winter distribution 1995–2000
- Winter abundance 1995–2000
- Breeding distribution 2007–2012
- Summer abundance 2007–2012
- Winter distribution 2007–2012
- Winter abundance 2007–2012
- Breeding distribution change
- Summer abundance change
- Winter distribution change
- Winter abundance change
More Long-eared Owl maps
- Breeding distribution 1995–2000
- Summer abundance 1995–2000
- Winter distribution 1995–2000
- Winter abundance 1995–2000
- Breeding distribution 2007–2012
- Summer abundance 2007–2012
- Winter distribution 2007–2012
- Winter abundance 2007–2012
- Breeding distribution change
- Summer abundance change
- Winter distribution change
- Winter abundance change
More maps for this atlas
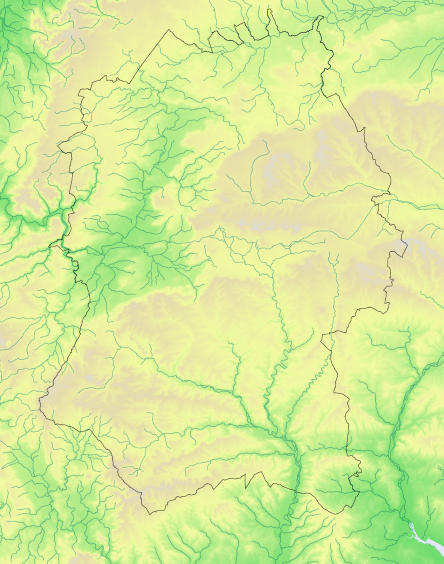
Map explanation
This map shows the breeding season distribution of the species in Wiltshire as revealed by the shared fieldwork for Bird Atlas 2007-2011 (BTO 2013) and for Wiltshire Tetrad Atlas 2007-2012.
Key
Data not mapped to preserve confidentiality
Long-eared Owls breed in North America from Canada to Mexico, across Europe (except the far north) and central Asia to Japan, and locally in northwest and sub-Saharan Africa. The northernmost breeders are migratory, wintering in or beyond the south of the species' summer range.
In Great Britain, Bird Atlas 2007-2011 recorded the species present in the breeding season in 18% of tetrads (a reduction of nearly a fifth since the 1968-72 Breeding Atlas), mostly in eastern and northern England and the lowland areas of Scotland.
In Wiltshire Long-eared Owls were scarce breeders in the first half of the 19th century but later in the century their numbers increased, possibly as a result of human persecution of Tawny Owls (their main competitors) and also because of the maturing of plantations that provided suitable nesting habitat. Then in the 20th century numbers decreased again. Birds of Wiltshire recorded them present in twelve 10km squares, with breeding in seven of them. Bird Atlas 2007-2011 recorded them in nine 10km squares, with breeding confirmed in only one.
References
The following references are used throughout these species accounts, in the abbreviated form given in quotation marks:
“1968-72 Breeding Atlas” – Sharrack, J.T.R. 1976: The Atlas of Breeding Birds in Britain and Ireland. T. & A. Poyser
“1981-84 Winter Atlas” – Lack, P.C. 1986: The Atlas of Wintering Birds in Britain and Ireland. T. & A. Poyser
“1988-91 Breeding Atlas” – Gibbons, D.W., Reid, J.B. & Chapman, R.A. 1993: The New Atlas of Breeding Birds in Britain and Ireland 1988-91. T. & A. Poyser
“Birds of Wiltshire” – Ferguson-Lees, I.J. et al. 2007 : Birds of Wiltshire, published by the tetrad atlas group of the Wiltshire Ornithological Society after mapping fieldwork 1995-2000. Wiltshire Ornithological Society.
“Bird Atlas 2007-2011” – Balmer, D.E., Gillings, S., Caffrey, B.J., Swann, R.L., Downie, I.S. and Fuller, R.J. 2013: Bird Atlas 2007-2011: the Breeding and Wintering Birds of Britain and Ireland
“WTA2” – ("Wiltshire Tetrad Atlas 2 ") the present electronic publication, bringing together the Wiltshire data from “Birds of Wiltshire” and “Bird Atlas 2007-11”, together with data from further fieldwork carried out in 2011 and 2012.
"Hobby" - the annual bird report of the Wiltshire Ornithological Society.